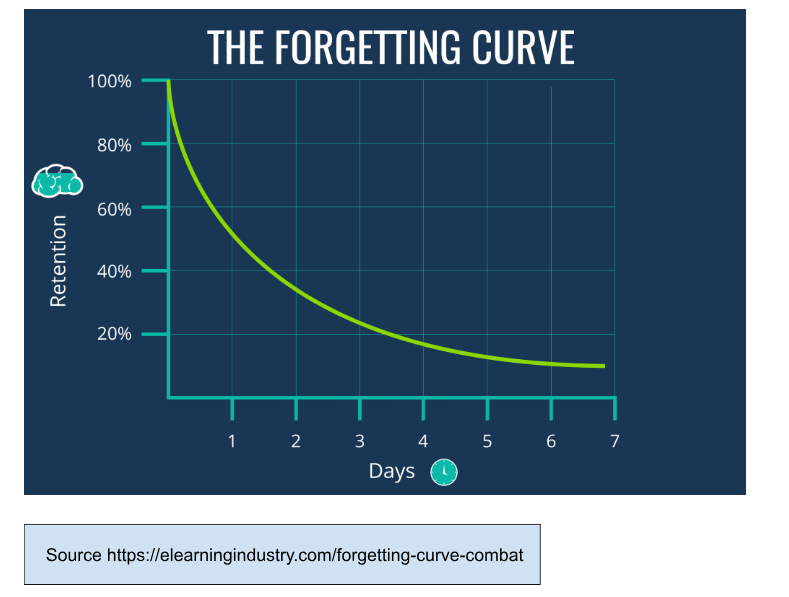
Nowadays, we tend to forget the important information that we obtained throughout the day. For example, you’re not going to remember what you ate for lunch a week ago or what you learned in a class three weeks ago if you don't actively recall the information. This phenomenon is called the “Forgetting Curve”.
The Forgetting Curve is a memory experiment founded by Hermann Ebbinghaus around 1880–1885. He conducted this research because there are still limited sources in this field of study at that time, and he wants to identify the factors that contribute to memory loss by experiencing it himself. In this experiment, he found that the human brain tends to subconsciously forget. This is because the brain cannot choose which information is important unless it is stored in the long-term memory. In a nutshell, this experiment proves how we lose information over time if we don’t try to retain it. This is a natural phenomenon because the brain works like a muscle and needs to be trained for a stronger memory.
There are a few things that you can do to decrease the Forgetting Curve. For instance, there is the Spaced Repetition technique and the Active Recall technique.
SPACED REPETITION
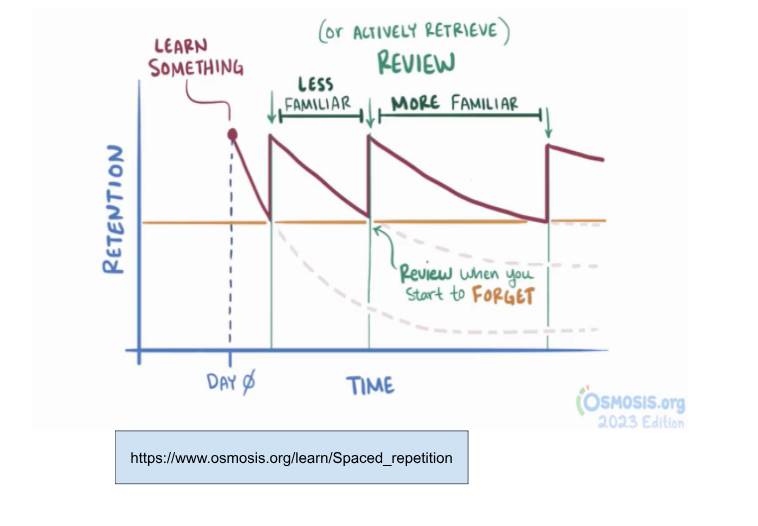
Spaced Repetition simply means to re-learn what you studied yesterday, but with a specific timeline or strategy. You can begin by learning something that's less familiar, so your brain is being trained to grasp unfamiliar terms. After that, make a specific timeline for repetition—you can try a 3-day interval for example. To fill this 3-day interval, you will be reviewing important materials after 24 hours of first learning it. Then, during the next interval, try learning something that you are already familiar with. Repeat the two intervals until your memories have improved. If the material now feels easy to you, you can adjust the interval to be longer or change the learning subject.
In theory, Spaced Repetition is a simple concept. However, in practice, Spaced Repetition is not as easy to follow through if you’re not persistent with your progress. For it to be effective, here are some tips: firstly, the intervals between repetitions must remain consistent. Secondly, even if it feels like there isn’t any progress being made at first, believe in yourself that there will be improvement. If you make Spaced Repetition a habit, this technique will be useful for any form of learning.
ACTIVE RECALL
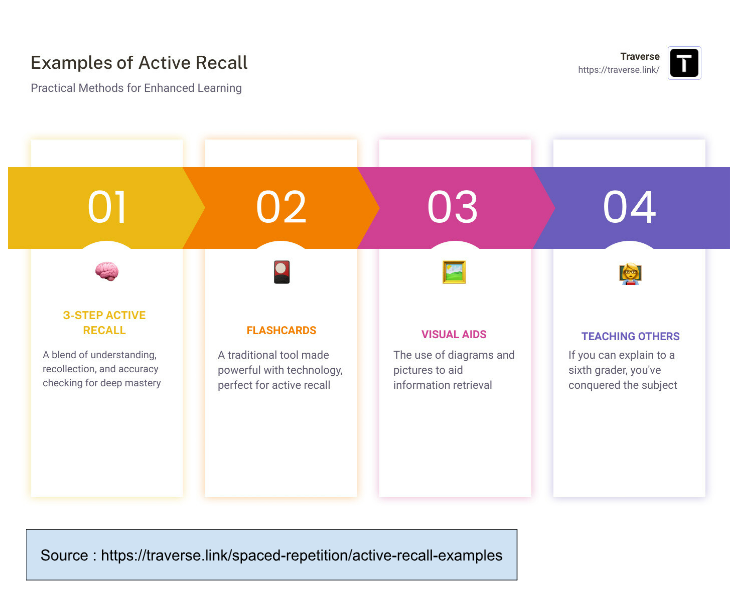
Active Recall means to recall our memories about certain topics with a few steps, it’s basically a part of Spaced Repetition itself. If Spaced Repetition is about timelines and intervals, Active Recall is about an actual learning technique to grasp information. There are a few choices of practical techniques for this method: flashcards, visual aids, or by teaching others. You can use flashcards and visual aids in the chapter that you’re unfamiliar with. Meanwhile, you can teach others in the chapter that you find easy—don't forget to ask feedback from the person you are explaining to, though. If your lecture is clear enough, it means that you’ve mastered that chapter.
These kinds of learning techniques can be applied to almost every form of learning, especially academic ones. You can divide materials and master them chunk by chunk instead of learning everything in one night and forgetting it the next day. This is because the learned materials are being stored in the long-term memory.
References :
Dr. John Wittman. (n.d.). The Forgetting Curve. Https://Www.Csustan.Edu/Sites/Default/Files/Groups/Writing%20Program/Forgetting_curve.Pdf, 1–2.
Harry Cloke. (2018, March 30). What Is The Forgetting Curve (And How Do You Combat It)? Https://Elearningindustry.Com/Forgetting-Curve-Combat.
Sander Tamm. (2023, January 30). Spaced Repetition: A Guide to the Technique. Https://E-Student.Org/Spaced-Repetition/.
Tiny Medicine. (2022). How to do ACTIVE RECALL Effectively? (4 Techniques worked for me). In https://youtu.be/IyvlgRf7u3Y?si=XX2SM-XfzSYqk8Uw.
The Forgetting Curve is a memory experiment founded by Hermann Ebbinghaus around 1880–1885. He conducted this research because there are still limited sources in this field of study at that time, and he wants to identify the factors that contribute to memory loss by experiencing it himself. In this experiment, he found that the human brain tends to subconsciously forget. This is because the brain cannot choose which information is important unless it is stored in the long-term memory. In a nutshell, this experiment proves how we lose information over time if we don’t try to retain it. This is a natural phenomenon because the brain works like a muscle and needs to be trained for a stronger memory.
There are a few things that you can do to decrease the Forgetting Curve. For instance, there is the Spaced Repetition technique and the Active Recall technique.
SPACED REPETITION
Spaced Repetition simply means to re-learn what you studied yesterday, but with a specific timeline or strategy. You can begin by learning something that's less familiar, so your brain is being trained to grasp unfamiliar terms. After that, make a specific timeline for repetition—you can try a 3-day interval for example. To fill this 3-day interval, you will be reviewing important materials after 24 hours of first learning it. Then, during the next interval, try learning something that you are already familiar with. Repeat the two intervals until your memories have improved. If the material now feels easy to you, you can adjust the interval to be longer or change the learning subject.
In theory, Spaced Repetition is a simple concept. However, in practice, Spaced Repetition is not as easy to follow through if you’re not persistent with your progress. For it to be effective, here are some tips: firstly, the intervals between repetitions must remain consistent. Secondly, even if it feels like there isn’t any progress being made at first, believe in yourself that there will be improvement. If you make Spaced Repetition a habit, this technique will be useful for any form of learning.
ACTIVE RECALL
Active Recall means to recall our memories about certain topics with a few steps, it’s basically a part of Spaced Repetition itself. If Spaced Repetition is about timelines and intervals, Active Recall is about an actual learning technique to grasp information. There are a few choices of practical techniques for this method: flashcards, visual aids, or by teaching others. You can use flashcards and visual aids in the chapter that you’re unfamiliar with. Meanwhile, you can teach others in the chapter that you find easy—don't forget to ask feedback from the person you are explaining to, though. If your lecture is clear enough, it means that you’ve mastered that chapter.
These kinds of learning techniques can be applied to almost every form of learning, especially academic ones. You can divide materials and master them chunk by chunk instead of learning everything in one night and forgetting it the next day. This is because the learned materials are being stored in the long-term memory.
References :
Dr. John Wittman. (n.d.). The Forgetting Curve. Https://Www.Csustan.Edu/Sites/Default/Files/Groups/Writing%20Program/Forgetting_curve.Pdf, 1–2.
Harry Cloke. (2018, March 30). What Is The Forgetting Curve (And How Do You Combat It)? Https://Elearningindustry.Com/Forgetting-Curve-Combat.
Sander Tamm. (2023, January 30). Spaced Repetition: A Guide to the Technique. Https://E-Student.Org/Spaced-Repetition/.
Tiny Medicine. (2022). How to do ACTIVE RECALL Effectively? (4 Techniques worked for me). In https://youtu.be/IyvlgRf7u3Y?si=XX2SM-XfzSYqk8Uw.
Content Writer : Wamey Lintang Ayu Pradnya Paramitha
Editor : Khaylila Jasmin Devani

.png)
Comments
Post a Comment